Key Takeaways:
- A SKU (Stock Keeping Unit) is a unique alphanumeric code (typically 8–10 characters) that you assign to each product or variant in your Amazon inventory. It links your listing to your internal tracking.
- You can either enter a custom SKU when creating a product listing in Seller Central or leave the SKU field blank and let Amazon generate it automatically.
- External traffic works best when paired with listing optimization , attribution tracking, and structured launch timing
- Use a clear, consistent format for SKUs (e.g., including category, color, size, or batch info) and avoid confusing characters. Each SKU must be unique and is limited to 40 characters.
- SKUs streamline inventory tracking and order fulfillment. Properly structured SKUs help prevent stockouts and keep your Amazon catalog organized as you scale.
When launching or adding products on Amazon, setting up SKUs correctly is essential for maintaining inventory accuracy and operational control.
A SKU serves as your internal identifier for each product or variation, linking listings to your inventory, fulfillment, and reporting systems.
Clear, well-structured SKUs help prevent tracking errors, simplify order management, and support smoother scaling as your catalog grows.
Whether you assign SKUs manually or allow Amazon to generate them, the way SKUs are created has a direct impact on how efficiently your Amazon business operates.
What are Amazon SKUs?
A SKU is a seller-created identifier tied to your Amazon listing. It does not have to match the ASIN or UPC – you choose it to fit your organization. For example, you might use TSHIRT-BLK-L-RA to denote a black large t-shirt from vendor “RA.”
Generally, SKUs help keep your inventory organized and track features like color or size. Every distinct product or variation needs its own SKU, which appears in your inventory records (but is hidden from customers).
By contrast, if you skip the SKU during listing, Amazon will still assign one for you.
How To Create Seller-Generated SKUs for Amazon (Custom SKUs)?
Creating your own SKU gives you control and consistency. To do this in Seller Central:
- Log in to Seller Central and navigate to Catalog > Add Products.
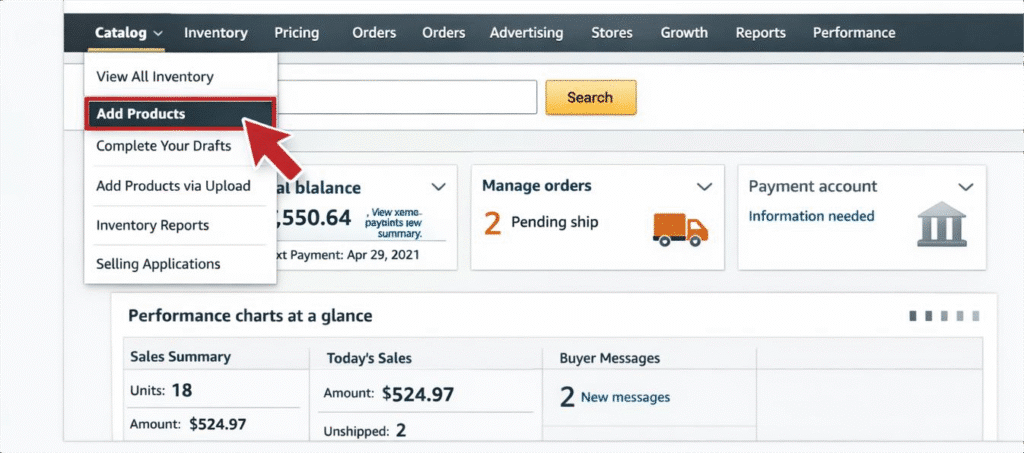
- Select or create your product listing. If the product already exists, search for it and click “Sell this product.” If it’s a new item, choose “I’m adding a product not sold on Amazon.”
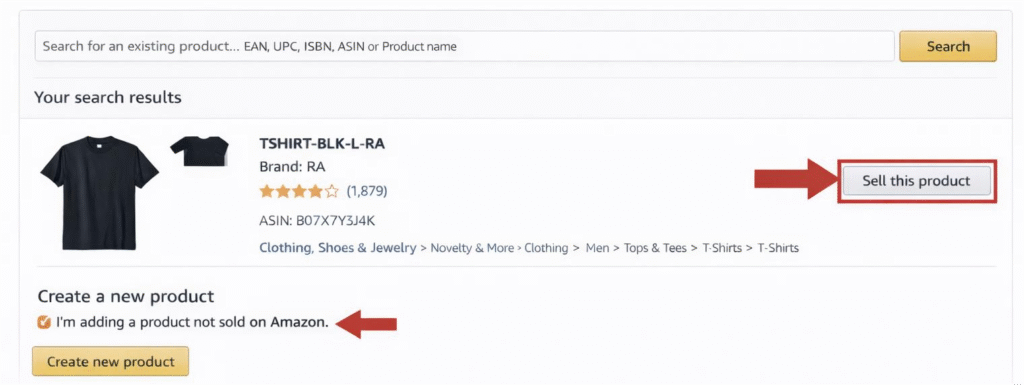
- Enter all required product details (title, category, UPC/GTIN, images, description, etc.).
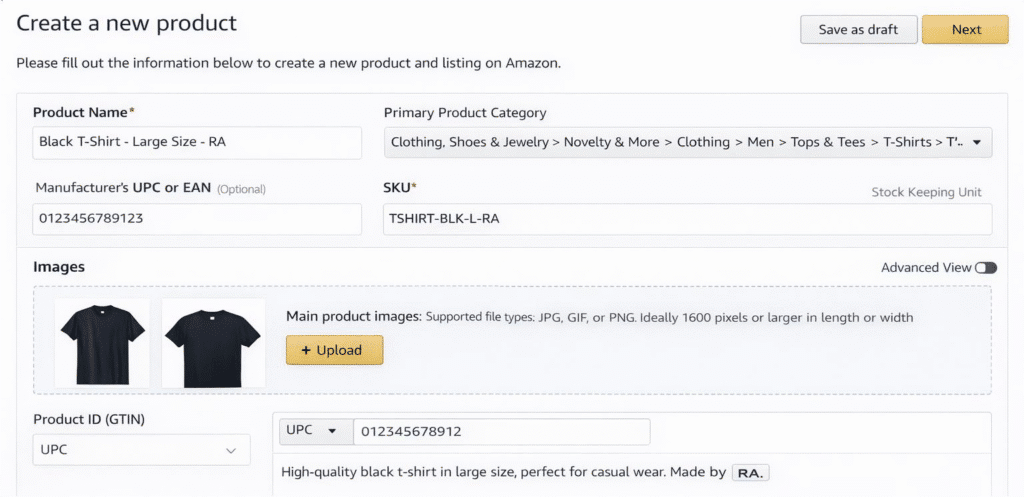
- In the SKU field, type your unique code. For example, incorporate key attributes (brand, category, color, size) separated by hyphens or underscores. Use only letters (A–Z), numbers (0–9), hyphens, or underscores – no spaces or special symbols.
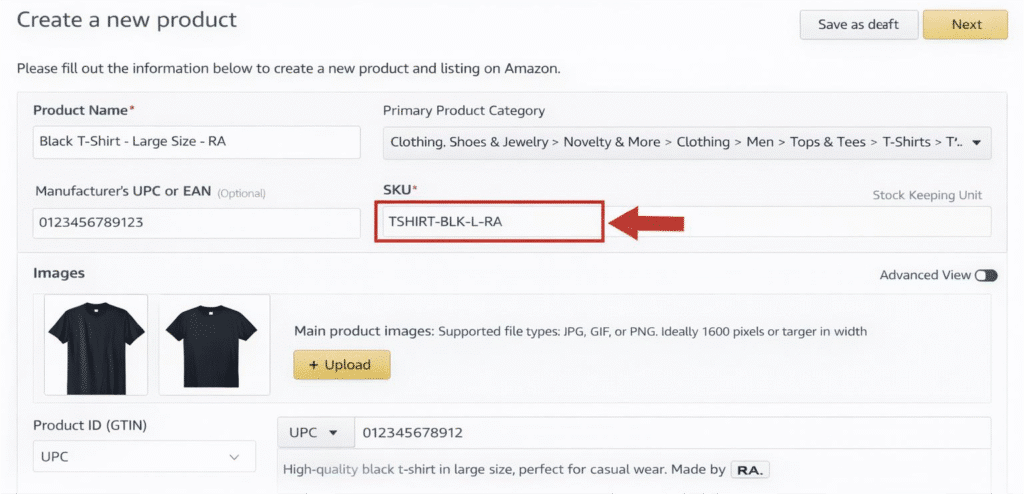
- Review and submit the listing. Once saved, Amazon will use your SKU as the product’s identifier in inventory.
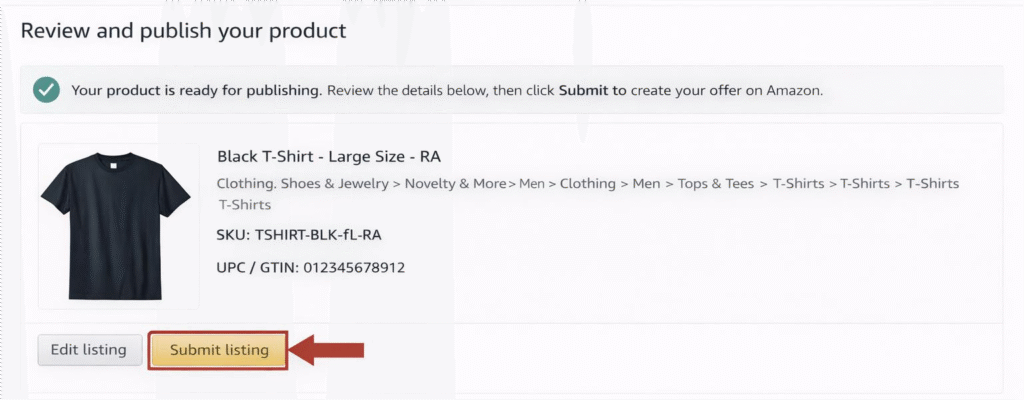
By following these steps, your new SKU (e.g., SHIRT-RDY-XL-RA1) instantly links to that ASIN. You can then see it in Manage Inventory, reports, and fulfillment workflows.
According to Amazon’s guidelines, SKUs can be up to 40 characters, but keeping them shorter (under 30) helps avoid errors.
Amazon-Generated SKUs
If you prefer not to invent your own code, Amazon can auto-assign SKUs during listing. To use an Amazon-generated SKU:
- Follow steps 1–3 above (log in, go to Add Products, and enter product info).
- When you reach the SKU field, leave it blank or click the Amazon-Generated option (if available).
- Save and finish the listing. Amazon will create a unique SKU for you and attach it to the product.
This approach is quick, especially for large catalogs. However, it produces random codes that may differ across marketplaces, making cross-channel tracking harder.
Experienced sellers often use custom SKUs for consistency.
Best Practices for Amazon SKUs
- Be consistent: Use the same SKU format across your Amazon accounts and other sales channels (Shopify, Walmart, etc.). For example, start with a category or vendor prefix (e.g., “SH” for shirts) followed by size or color codes. Document your format rules and train your team to follow them.
- Include meaningful info: A well-structured SKU might encode product type, size, color, or supplier. For instance, BK-TSHIRT-BL-L tells you it’s a black large t-shirt in the “BK” category. This makes manual sorting and analysis easier.
- Avoid confusing characters: Do not use spaces, and steer clear of letters/numbers that look alike (like O vs 0, I vs 1). Always use all caps or a consistent style.
- Unique & permanent: Never reuse a SKU for a different product. Once a SKU is assigned (even if you delete the listing), Amazon prevents reusing it. If a product version changes, create a new SKU.
- Use tools: For large inventories, consider using inventory management software (InventoryLab, etc.) to generate and sync SKUs across systems.
Common SKU Mistakes That Hurt Amazon Sellers
| Common SKU Mistake | Why It Hurts Sellers |
| Using auto-generated SKUs | Random codes make tracking and analysis difficult |
| Changing SKU formats | Breaks data consistency and reporting |
| Reusing SKUs | Causes inventory and fulfillment errors |
| No planning for variations | Creates confusion when the catalog expands |
| Confusing characters | Leads to manual and system errors |
How Strategic SKUs Support Successful Amazon Product Launches?
For brands launching new products, SKUs play a bigger role than most realize. A clean, well-planned SKU structure helps teams stay organized and make smarter decisions from day one.
- Track launch-phase sales accurately: Strategic SKUs allow you to separate launch data from long-term performance. This makes it easier to see how a product is performing during its critical early weeks, measure the impact of launch campaigns, and understand true demand without data confusion.
- Monitor early inventory velocity: With clear SKUs in place, brands can track how fast each product or variation is selling. This helps prevent early stockouts or over-ordering, both of which can hurt momentum and profitability during the launch phase.
- Identify winning variations faster: When each variation has a distinct SKU, performance comparisons become much clearer. Brands can quickly see which sizes, colors, bundles, or formulations are resonating with customers and double down on what’s working.
- Align PPC data with product performance: Well-structured SKUs make it easier to connect advertising data with actual sales results. This allows brands to optimize ad spend, pause underperforming campaigns, and scale winning keywords with confidence.
At scale, SKUs are not just identifiers—they become decision-making tools that influence inventory planning, ad strategy, and product optimization.
Experienced Amazon agencies like Amerify design SKU systems that support long-term growth, not just basic listing creation and SEO, ensuring brands are set up for sustainable success from launch onward.
Conclusion
Assigning SKUs correctly is a small step that pays off in smoother inventory management and more efficient product launches. Whether you create your own SKUs or let Amazon generate them, be sure to follow best practices: unique codes, a logical format, and consistent use across your catalog.
Amerify’s Full Service Management specialists can help you set up and optimize your SKUs (and every other part of your product listing). Contact us for a free consultation to ensure your new products hit the ground running on Amazon. Let Amerify handle the details so you can focus on growing your brand! Contact us now!



